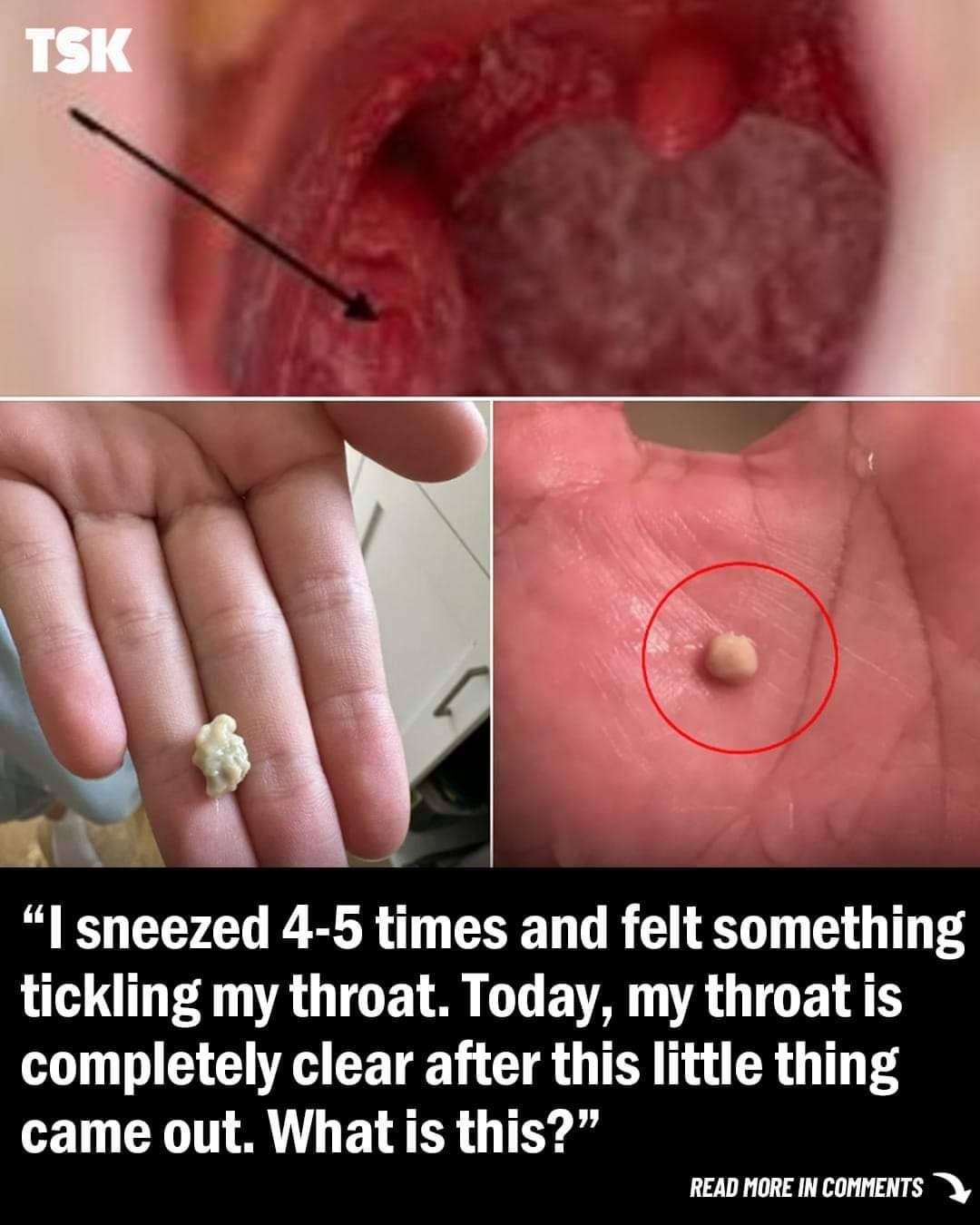
Tonsil stones, or tonsilloliths, are small, calcified deposits that form in the crevices of your tonsils. While often harmless, they can lead to discomfort and bad breath. This comprehensive guide delves into the causes, symptoms, and treatments of tonsil stones, providing valuable insights into managing and preventing this common condition.
What Are Tonsil Stones?
Tonsil stones are hard formations that develop when debris such as food particles, dead cells, and bacteria become trapped in the tonsillar crypts—small pockets in your tonsils. Over time, this debris calcifies, forming stones that can vary in size.
Common Causes of Tonsil Stones
Several factors contribute to the formation of tonsil stones:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate dental care can lead to the accumulation of debris and bacteria in the mouth, increasing the risk of tonsil stones.
- Chronic Tonsillitis: Frequent inflammation of the tonsils can enlarge the tonsillar crypts, making it easier for debris to become trapped.
- Sinus Issues: Conditions that cause excess mucus production can result in mucus getting caught in the tonsils, leading to stone formation.
- Large Tonsils: Individuals with naturally larger tonsils have more crevices where debris can accumulate.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Tonsil stones may not always cause noticeable symptoms, especially when small. However, larger stones can lead to:
- Bad Breath (Halitosis): The accumulation of bacteria in tonsil stones often results in persistent bad breath.
- Sore Throat: Stones can cause irritation and discomfort in the throat.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Large stones may obstruct swallowing, leading to pain or a feeling of something stuck in the throat.
- Ear Pain: Due to shared nerve pathways, tonsil stones can cause referred pain to the ears.
- Visible White or Yellow Debris: Stones may appear as white or yellowish spots on the tonsils.
Diagnosing Tonsil Stones
Healthcare providers typically diagnose tonsil stones through:
- Physical Examination: Visual inspection of the mouth and throat can reveal visible stones.
- Imaging Tests: If stones are not easily seen, imaging techniques like CT scans or X-rays can help identify them.
Effective Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the size and symptoms of the tonsil stones:
- Home Remedies:
- Gargling with Salt Water: Regular gargling can help dislodge small stones and soothe throat discomfort.
- Manual Removal: Gently using a cotton swab or toothbrush to remove stones can be effective but should be done cautiously to avoid injury.
- Medical Treatments:
- Laser Tonsil Cryptolysis: A procedure that uses lasers to reduce the size of tonsillar crypts, minimizing stone formation.
- Tonsillectomy: Surgical removal of the tonsils is considered in severe or recurrent cases.
- Antibiotics: Prescribed to reduce bacterial buildup, though they don’t address the underlying cause.
Preventing Tonsil Stones
To reduce the risk of developing tonsil stones:
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush and floss regularly to minimize debris and bacteria in the mouth.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps keep the mouth clean and prevents debris buildup.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can contribute to dry mouth and increase the risk of stone formation.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Persistent or Severe Symptoms: Ongoing discomfort, difficulty swallowing, or severe pain.
- Recurrent Tonsil Stones: Frequent formation of stones despite preventive measures.
- Signs of Infection: Symptoms like fever, swelling, or redness around the tonsils.
Conclusion
Tonsil stones, while often harmless, can cause discomfort and other symptoms. Understanding their causes and symptoms is crucial for effective management. By maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking appropriate treatment when necessary, you can reduce the occurrence of tonsil stones and maintain better oral health.





