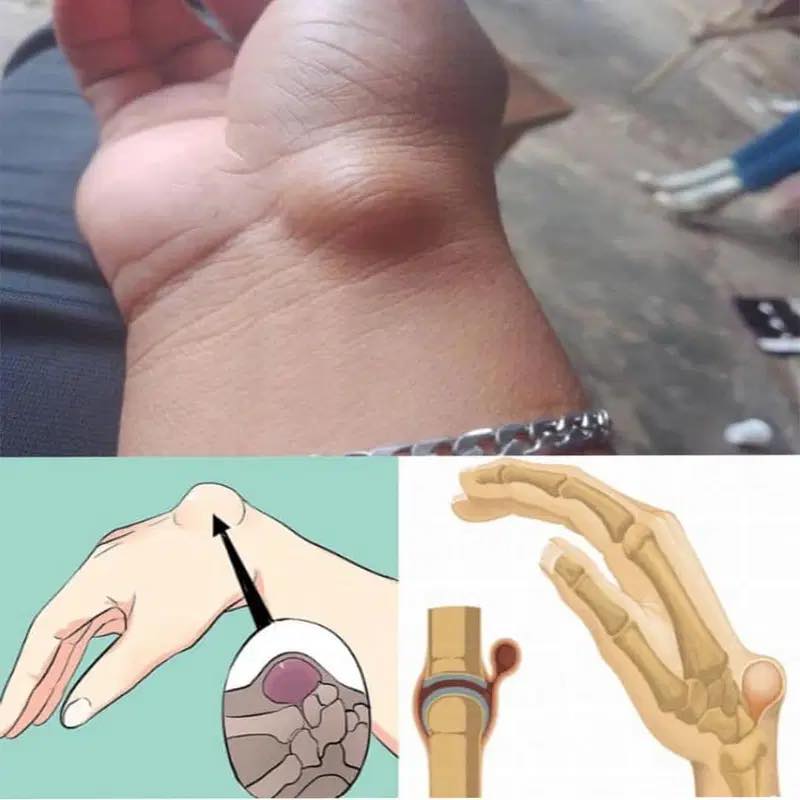
Have you ever noticed a soft, sometimes tender lump on your wrist that seems to appear out of nowhere? This could be a wrist ganglion cyst—a common, noncancerous swelling that often develops along the tendons or joints of your wrists or hands. While generally harmless, these cysts can cause discomfort and may interfere with joint movement. This article delves into the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options for wrist ganglion cysts.
What Is a Wrist Ganglion Cyst?
A wrist ganglion cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms near a joint or tendon, most commonly on the back (dorsal side) or front (volar side) of the wrist. These cysts are filled with synovial fluid—the lubricating fluid that surrounds joints and tendons. Although they are benign and not cancerous, ganglion cysts can vary in size and may fluctuate over time.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of ganglion cysts remains unclear, but several factors may contribute to their development:
-
Repetitive Wrist Movements: Engaging in activities that involve repetitive wrist motions, such as typing, playing certain sports, or using handheld devices, can increase the risk of developing these cysts.
-
Joint or Tendon Injury: Previous injuries to the wrist joints or tendons may predispose individuals to ganglion cyst formation.
-
Arthritis: Osteoarthritis, particularly affecting the finger joints closest to the fingernails, has been associated with a higher incidence of ganglion cysts.
-
Age and Gender: Ganglion cysts are more commonly observed in individuals between the ages of 15 and 40 and are more prevalent in women than men.
Recognizing the Symptoms
While some ganglion cysts cause no noticeable symptoms, others can lead to:
-
Visible Lump: A palpable, round, or oval lump that is typically soft and immobile.
-
Pain or Discomfort: If the cyst presses on nerves, it can cause pain, tingling, or muscle weakness.
-
Limited Mobility: Depending on its size and location, a ganglion cyst may restrict joint movement.
Diagnosis
To diagnose a ganglion cyst, a healthcare provider may:
-
Physical Examination: Assess the lump’s appearance and palpate it to evaluate its consistency and tenderness.
-
Imaging Tests: Ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be used to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options
Treatment for a ganglion cyst depends on factors such as the severity of symptoms and the cyst’s impact on daily activities. Options include:
-
Observation: If the cyst is painless and does not interfere with movement, a “watch and wait” approach may be recommended, as some cysts resolve on their own.
-
Immobilization: Wearing a wrist brace or splint can help restrict movement, potentially reducing the size of the cyst and alleviating symptoms.
-
Aspiration: In this procedure, a doctor uses a needle to drain the fluid from the cyst. While this can provide relief, the cyst may recur since the underlying structure remains.
-
Surgical Removal: If conservative treatments fail and the cyst is causing significant discomfort or limiting function, surgical excision may be considered. This involves removing the cyst along with a portion of the joint capsule or tendon sheath to reduce the likelihood of recurrence.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional if you experience:
-
Persistent pain or discomfort.
-
A lump that changes in size or becomes increasingly painful.
-
Difficulty using your hand or wrist due to the cyst.
Early evaluation can help determine the appropriate course of action and prevent potential complications.
Conclusion
Wrist ganglion cysts are common, benign lumps that can cause discomfort and interfere with daily activities. Understanding the potential causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring the available treatment options can help manage this condition effectively. If you suspect you have a ganglion cyst, consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach tailored to your specific situation.





