Blood clots are a serious health concern that can lead to life-threatening conditions if not promptly addressed. Understanding the signs and symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment. This article aims to shed light on the various manifestations of blood clots and emphasize the importance of seeking immediate medical attention when these symptoms arise
Understanding Blood Clots
A blood clot, medically known as a thrombus, is a mass of blood that has changed from a liquid to a gel-like or semisolid state. While clotting is a necessary process to prevent excessive bleeding, clots that form inappropriately within blood vessels can obstruct blood flow, leading to serious complications. Clots can develop in both veins and arteries, each presenting distinct symptoms and risks.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): The Hidden Threat
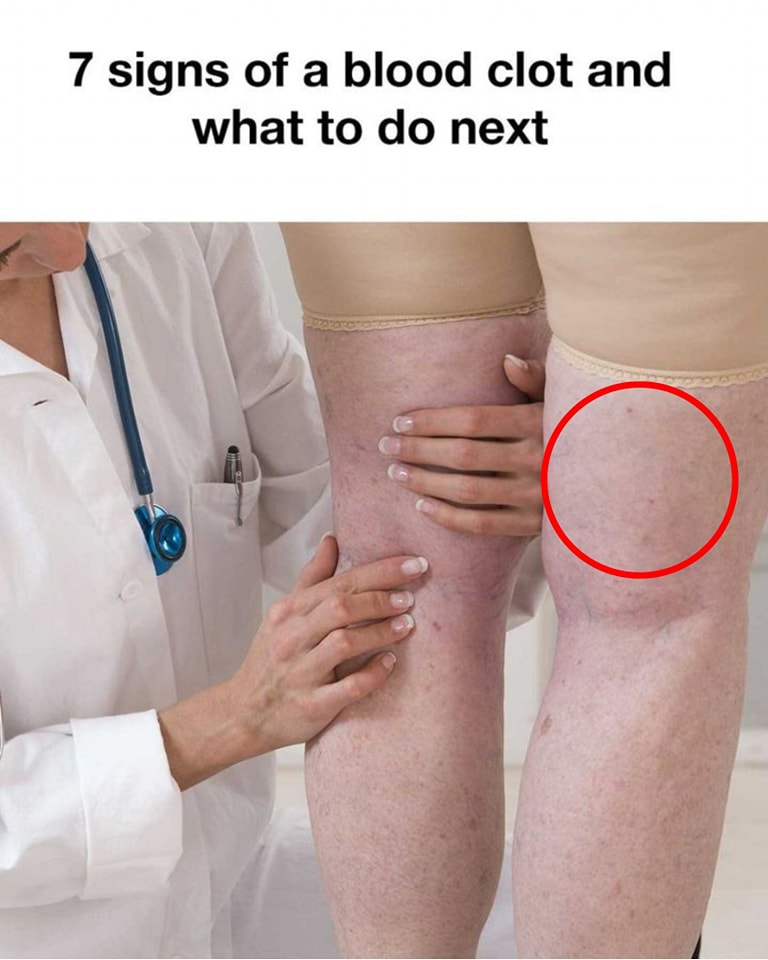
DVT occurs when a clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs. This condition can be asymptomatic, but often presents with:
-
Swelling in one leg: A noticeable increase in size, often accompanied by tightness.Pain or tenderness: A cramp-like sensation, especially when standing or walking.
-
Warmth and redness: The affected area may feel warmer than the surrounding skin and appear reddened.
These symptoms result from the clot obstructing blood flow, causing blood to pool behind the blockage.

Pulmonary Embolism (PE): When Clots Travel
A PE occurs when a clot breaks free and travels to the lungs, blocking a pulmonary artery. This is a medical emergency, with symptoms including:
-
Sudden shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing without exertion.
-
Chest pain: Sharp, stabbing pain that may worsen with deep breaths.
-
Rapid heart rate: A racing heartbeat, even at rest.
-
Coughing: Possibly producing blood-tinged sputum.
These signs indicate that a clot is impeding blood flow in the lungs, reducing oxygen levels and straining the heart.
Arterial Clots: Blocking Vital Pathways
Clots in arteries can obstruct blood flow to critical organs, leading to:
-
Heart attack: Characterized by chest pain, shortness of breath, and discomfort in the upper body.
-
Stroke: Symptoms include sudden numbness or weakness, especially on one side of the body, confusion, trouble speaking, and vision problems.
These events require immediate medical intervention to restore blood flow and minimize damage.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Several factors increase the risk of developing blood clots:
-
Prolonged immobility: Extended periods of inactivity, such as long flights or bed rest.
-
Surgery or injury: Particularly orthopedic procedures.
-
Medical conditions: Cancer, heart disease, and clotting disorders.
-
Lifestyle factors: Smoking, obesity, and certain medications like birth control pills.
Preventative measures include staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, and following medical advice regarding medications and lifestyle changes.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of the aforementioned symptoms, especially if they appear suddenly or worsen rapidly, seek emergency medical care. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent serious complications or death.
Being aware of the signs and symptoms of blood clots empowers you to take prompt action, potentially saving your life or the lives of others. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and don’t hesitate to seek medical help when needed.





